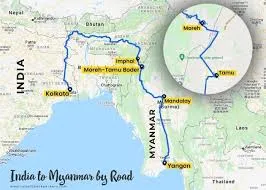
GlobalFootprint: Manipur serves as India’s “gateway to the East,” with the border town Moreh being the only feasible land route for trade between India and Myanmar (and thus a link to Southeast Asia). Period: This strategic location has existed historically; in recent years the push under the “Act East” policy and infrastructure improvements have increased its importance. Impact: • Strengthens Manipur’s potential in cross-border trade and global supply chains via ASEAN connectivity. • Opens up export and import corridors, making Manipur part of a larger regional economic network. • Drives infrastructure development (roads, rail, border facilities) that benefit local industry and trade.
Link : https://ibef.org/states/manipur-presentation?utm_source=chatgpt.com



GlobalFootprint: Manipur’s agrarian base includes horticulture crops (pineapple, passion fruit, black rice), bamboo, vegetables, and has export potential. The state is one of India’s large bamboo-producing states (55 species, 14 % of country’s stock) which also has industrial/export relevance. Period: Ongoing; recent years have seen increased focus on agro-processing and value addition. Impact: • Provides livelihoods in large parts of rural Manipur via agriculture & horticulture. • Creates export-ready opportunities for niche Himalayan/NE products (e.g., black rice, passion fruit, bamboo) targeting global markets. • Encourages development of processing, logistics, value-chain infrastructure (cold chains, packaging) in the state.
Link : https://www.nabard.org/auth/writereaddata/tender/MAN_Thoubal_Kakching.pdf?utm_source=chatgpt.com



Global Footprint: Manipur is known for its large number of handicraft units and artisan workforce; handloom is the largest cottage industry in the state. Also, bamboo and cane industries offer export and international design linkages. Period: Traditional craft economy long-standing; export and modernisation efforts increasing in the 2020s. Impact: • Preserves cultural heritage and provides employment in less-industrialised/hill areas. • Offers export potential for artisanal textiles, bamboo/cane products, handicrafts to global markets. • Enhances brand value for Manipur as a state of craftsmanship and unique cultural goods.
Link : https://ibef.org/states/manipur-presentation?utm_source=chatgpt.com



GlobalFootprint: With rich biodiversity, scenic hills/valleys, and cultural heritage, Manipur is positioning itself as a tourism and eco-destination. For example, the Musi-lake/lake systems and forest areas attract visitors. Period: Recent push especially in 2010s-2020s with infrastructure improvements and awareness of global travel markets. Impact: • Creates jobs and incomes in tourism/hospitality, especially in rural and hill zones. • Promotes conservation of biodiversity and natural ecosystems via eco-tourism. • Raises global awareness of Manipur’s uniqueness, thereby attracting non-resident tourism and international travellers.
Link : https://ibef.org/states/manipur?utm_source=chatgpt.com



GlobalFootprint: Under the Indian government’s “Act East Policy”, Manipur’s strategic location next to Myanmar gives it potential as an investment & trade corridor connecting to Southeast Asia. The state also offers forest, bamboo, agro-resources - combining natural resource advantage with connectivity. Period: Gains prominence from mid-2010s onward; heightened focus in 2020s. Impact: • Opportunity for global investors and companies to use Manipur as a base for Asian market access. • Opening up of infrastructure (roads, rail, border trade) and policy reforms improve business environment. • Potential for cross-border industrial clusters, logistics hubs, and export zones that link India with Southeast Asia.
Link : https://ibef.org/states/manipur-presentation?utm_source=chatgpt.com